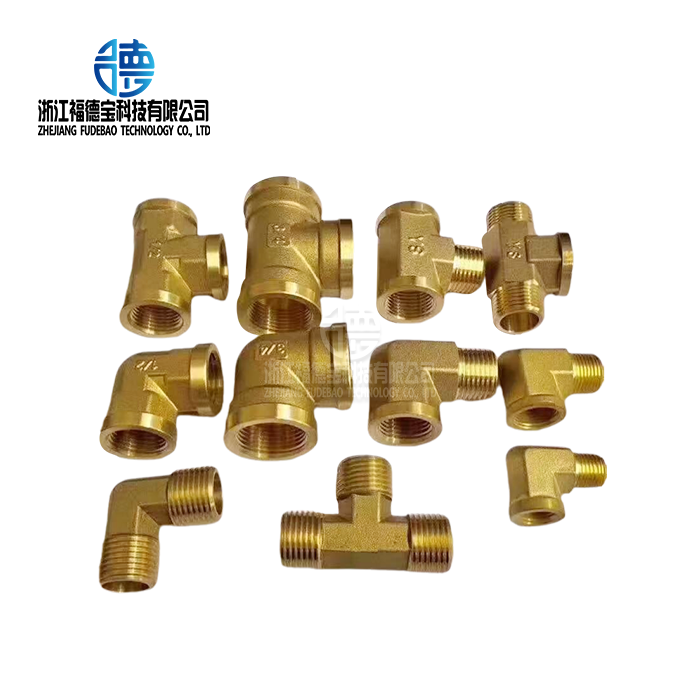
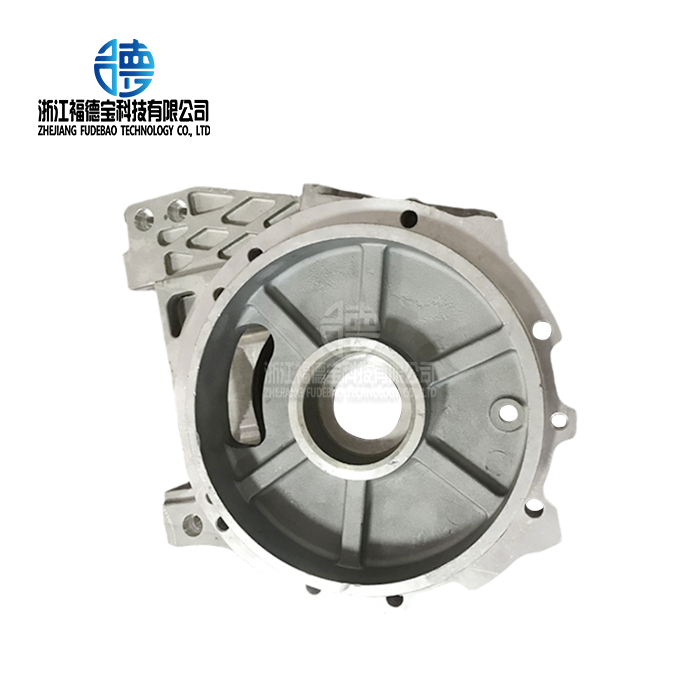
Making high-precision copper castings takes a lot of knowledge about metallurgy and the latest tools, as well as very strict quality control, to meet the high standards of today's industry uses. When high conductivity and rust protection are needed, these specialized parts are very important in electrical systems, naval uses, and cars. The precision casting method creates parts that meet very tight tolerances of ±0.05 mm, which guarantees the best performance in tough working conditions in many different fields. This is possible because of careful material choice, controlled melting, exact mold design, and lots of machining after casting.

Understanding Copper Castings in Modern Manufacturing
Copper castings are made by carefully melting and shaping raw copper into the exact shapes needed for commercial use. Pure copper and copper alloys work better than other metals and materials like bronze, brass, aluminum, or steel castings when it comes to conducting heat and electricity and resisting bacteria. This makes them very important for certain industrial situations.
Common Copper Alloy Compositions and Properties
Choosing the right copper metal formulas has a direct impact on how strong, resistant to rust, and conductive the final castings are. C11000, or pure copper, has the highest electrical conductivity at 101% IACS, but it can oxidize if you're not careful when casting it. Phosphor bronze is a copper-tin combination that is stronger, harder, and better at conducting electricity than its individual parts. Brass castings made from copper-zinc mixtures are easier and cheaper to make for uses where high conductivity isn't important.
Industrial Applications Driving Demand
These days, modern production industries are using copper castings more and more for situations where performance needs are more important than the cost of the materials. Marine gear is made from copper because it doesn't corrode in sea or get covered in biofouling. Electrical connecting housings and motor parts are made with copper so that they don't waste as much energy. The way copper manages heat helps keep the best working temperatures for precision machine parts in industrial tools. The car industry uses copper castings in electrical systems, heat exchanges, and specialized engine parts where performance and dependability are not up for debate.
The Complete Process of Manufacturing High-Precision Copper Castings
The process of making high-precision copper castings includes many specialized steps. Each one needs careful handling and expert knowledge to get the right dimensions and smooth surface that industrial uses need.
Pattern Design and Mold Preparation
The casting method starts with making a thorough mold that material loss, draft angles, and cutting adjustments. Engineers can use computer-aided design tools to see how filling patterns work and find possible places where defects might happen before they actually make something. Mold preparation means making hollow shapes with sand, clay, or metal tools based on the casting method that is used. Investment casting uses clay shell molds to make parts with complicated shapes, and sand casting uses resin-bonded sand systems to make bigger parts. Die casting needs to have exact shaped steel models that can handle heat cycles over and over again.
Melting and Pouring Operations
Copper melting needs a special furnace that can get hotter than 1200°C and control the atmosphere inside the furnace very carefully so that no rusting happens. Induction furnaces use electromagnetic stirring and even burning to make sure that the metal is the same throughout. Protective environment or vacuum melting keeps copper from oxidizing and the chemistry of the metal intact. To avoid defects, pouring must control the metal's temperature, the filling rate, and the commotion. Automated filling systems make things more consistent and keep people away from very hot activities.
Controlled Cooling and Heat Treatment
The way copper castings cool has a big impact on their mechanical qualities and how well they keep their shape. Using controlled cooling rates avoids thermal stress and keeps warping to a minimum in complicated shapes. Stress relief, annealing, and precipitation hardening are all heat treatments that make the material traits better for certain uses. Keeping an eye on the temperature and using controlled gas burners make sure that each batch of output has the same outcome.
Precision Machining and Finishing
Post-casting cutting processes are able to get the exact measurements needed for high-precision uses. CNC machine centers with specialized tools keep copper's unique cutting features in mind while keeping the accuracy of the dimensions. Surface finishing processes, like cutting, sanding, and soldering, get parts ready for the final assembly. Quality control during cutting makes sure that the work meets both scientific specs and business standards.

Advantages and Challenges of Copper Castings Compared to Alternatives
Even though copper castings cost more than other casting materials, they have unique benefits that make them the right choice. Understanding these benefits and the problems that come with them helps buying teams and engineering professionals make smart choices.
Performance Benefits of Copper Castings
Copper castings have a thermal conductivity of 200–400 W/mK, based on the makeup of the metal. This high thermal conductivity makes them great for getting rid of heat in thermal management systems. For casting metals, electrical conductivity close to 60% IACS makes them work well in electrical parts. It is more resistant to corrosion in aquatic and chemical settings than many other materials, which extends the service life of components. Being able to make complex shapes with thin walls and fine features lowers the cost of production and assembly.
Manufacturing and Cost Considerations
It takes a lot of thought to figure out if using copper metals is worth it for each purpose because they cost a lot more than aluminum, brass, or steel. Porosity, metal particles, and hot cracking are all casting flaws that need special quality management and process control. Alloys with lower melting points use less energy and tools compared to those with higher melting points. But in important situations where failure is not an option, the better performance often makes the higher price worth it.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Materials
Copper has better heat and electrical efficiency than aluminum castings, but it is heavier and more expensive. Bronze castings have similar protection to rust but are stronger and less conductive. Steel castings are stronger from a practical point of view, but they don't have copper's electrical qualities or resistance to rust. Brass castings have good enough conductivity for uses that aren't too demanding. They also cost less and are easier to machine.
Practical Considerations for Procuring High-Precision Copper Castings
To get high-precision copper castings, you need to know about the supplier's skills, how they ensure quality, and the costs that affect the success of the project and the possibility of a long-term relationship.
Supplier Selection Criteria
The beginning of source review is knowing how to make copper casting. ISO 9001, AS9100, and IATF 16949 are examples of certifications that show you are dedicated to quality management systems. The amount of work that can be done and the tools that are available must match the number and technical needs of the job. Being able to customize things, like getting help with engineering, making prototypes, or optimizing designs, adds value beyond just making things.
Understanding Pricing Drivers and Lead Times
Copper market conditions and metal standards affect material costs. Long-term contracts need to be able to adapt to price changes. The choice of casting method affects the cost of the tools. Investment casting has a higher upfront cost but a lower cost per piece for complex shapes. Unit price is affected by volume factors, as bigger amounts allow for more efficient processing and lower setup costs. It takes anywhere from 2 to 4 weeks for prototypes to be made and anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks for production tools and the first production runs.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Coordinate measuring machines, visual inspection systems, and other dimensional inspection tools make sure that technical limits are met. Material approval and metallurgy tests check the makeup and mechanical qualities of the material. Automotive PPAP paperwork needs a lot of quality planning and proof. Materials and processes can be tracked during the whole production cycle with the help of traceability tools.

Enterprise Introduction and Our Copper Casting Solutions
Zhejiang Fudebao Technology Co., Ltd. has built up a wide range of skills in high-precision copper casting and cutting services for uses with very high standards in the automobile, industrial, and electrical sectors. By using both advanced casting methods and exact CNC milling, our unified production method makes sure that all of the steps from turning raw materials into finished parts are done in-house.
Manufacturing Capabilities and Equipment
Our factory has specialized tools for working with copper alloys. These include high-frequency induction melting ovens, low-pressure casting machines, and precision die-casting systems. Automated CNC cutting centers and CNC lathes always get limits of ±0.05mm. Electroplating, anodizing, and adding protection coatings are all surface treatments that complete the finishing process. Coordinate measuring machines, steel testing labs, and other quality control tools make sure that foreign standards are met.
Technical Expertise and Certifications
Engineering support services include things like making designs better, analyzing moldflow, and making prototypes to cut down on the time and money needed for production and development. Our expert team helps with choosing products and improving processes based on how they will be used. Quality control systems and standards make sure that goods are always made in a way that meets the needs of the customer. We stay ahead of the competition in precision casting markets by constantly buying high-tech tools and teaching our staff.
Conclusion
Making high-precision copper castings takes a lot of technical knowledge, special tools, and strict quality control systems to meet the tough standards of today's industry uses. Because of their great conductivity and resistance to rust, copper metals are used in electrical, automobile, and naval uses where performance is key. To buy successfully, you need to know the whole manufacturing process, what suppliers can do, and the costs that affect the success of the project. The investment in accurate copper castings pays off in the long run by working better, lasting longer, and needing less upkeep in important uses.
FAQs
Which variables have the biggest effect on copper casting prices?
Choosing the material is the most important factor in cost, and pure copper and specialty metals are very expensive. The costs for each unit really depend on the production rate, the casting method's difficulty, and the standards that need to be met. Secondary processes like heat treatment, precision drilling, and surface finishing are often needed to meet performance standards, even though they raise the total cost of a component.
How do makers of copper castings make sure they are the right size?
Pattern creation that takes shrinking into account, controlled cooling to avoid warping, and precise cutting of important features all help to get dimensional accuracy. Statistical process control tracking and coordinate measure tools make sure that the work meets the requirements. In order to get the same results every time, experienced foundries keep the casting process within small ranges.
Which fields get the most benefit from using copper castings instead of other kinds of materials?
The electrical power creation industries use copper's great conductivity for motor parts and electrical links. Marine uses make use of natural resistance to rust in settings with salt water. Automotive electrical systems need copper's ability to carry electricity and dependability. Industrial heat exchangers make the best use of copper's ability to control heat.
Partner with Fudebao Technology for Premium Copper Casting Solutions
Zhejiang Fudebao Technology is ready to help you with precision copper casting because they have a lot of producing skills and technical knowledge. Our unified method uses both advanced casting and precision machining to meet even the most difficult requirements with full answers. Our skilled staff will help with engineering and make sure everything is high quality for the whole duration of your project, whether you need pilot development or full-scale production.
As a reliable producer of copper castings, we know how important it is for your uses to always get the same high quality. Our cutting-edge building and approved quality systems make sure that our supply chain partners can count on us for car, electrical, and industrial equipment. Our knowledge of materials and design improvement services help engineering teams get the best performance and cost-effectiveness.
Are you ready to talk about what you need for your precision copper casting? Our tech experts can look over your project details and come up with ways to help. To set up a meeting with us and learn how our knowledge of copper casting can improve your product and make your production process more efficient, email us at hank.shen@fdbcasting.com.
References
Davis, J.R. "Copper and Copper Alloys: ASM Specialty Handbook." ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 2001.
Campbell, John. "Complete Casting Handbook: Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design." Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2015.
Beeley, Peter R. "Foundry Technology." Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2001.
Stefanescu, Doru Michael. "Science and Engineering of Casting Solidification." Springer International Publishing, New York, 2015.
Brown, John R. "Foseco Non-Ferrous Foundryman's Handbook." Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 1999.
Ravi, B. "Metal Casting: Computer-Aided Design and Analysis." Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2005.












_1756346613780.webp)
_1756349071334.webp)



