Choosing the Right Sand Casting Supplier
2026-01-20
A crucial choice that might make or ruin your manufacturing operation is choosing the correct sand casting provider. One of the most adaptable and economical processes for creating intricate metal parts for a variety of industries is still sand casting. Working with the correct foundry guarantees dimensional precision, material integrity, and dependable delivery schedules that keep your production lines operating efficiently, whether you're sourcing automobile brackets, industrial equipment housings, or aerospace structural parts.

Understanding Sand Casting and Its Role in Manufacturing
The Fundamentals of Sand Casting Process
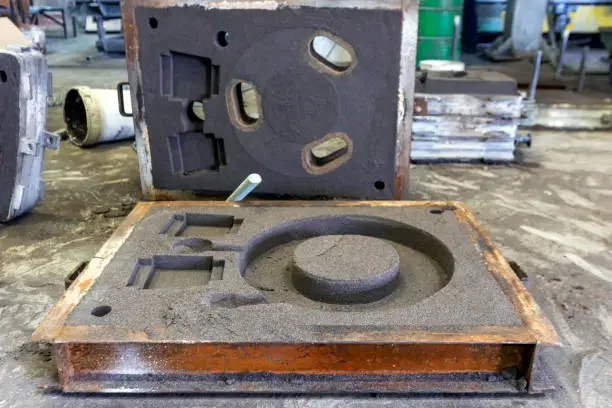
In sand casting, molten metal is poured into a mold cavity made of sand to create metal pieces. The first step in the process is pattern creation, which involves using wood, metal, or polymer materials to mimic the required part shape. Then, using gating devices to regulate metal flow and solidification patterns, foundry personnel fill the mold cavity surrounding the design with carefully prepared sand.
This casting method's flexibility comes from its ability to work with almost any metal alloy, from high-strength steel and cast iron to aluminum and copper. Depending on the needs of production, mold materials may be altered. For example, chemically bonded sands give better dimensional stability for precise applications, while green sand molds enable quick turnaround for prototypes. The quality of the finished item is directly impacted by temperature control throughout the pouring and cooling processes, therefore thermal management is essential for complicated geometries.
Industrial Applications and Material Capabilities
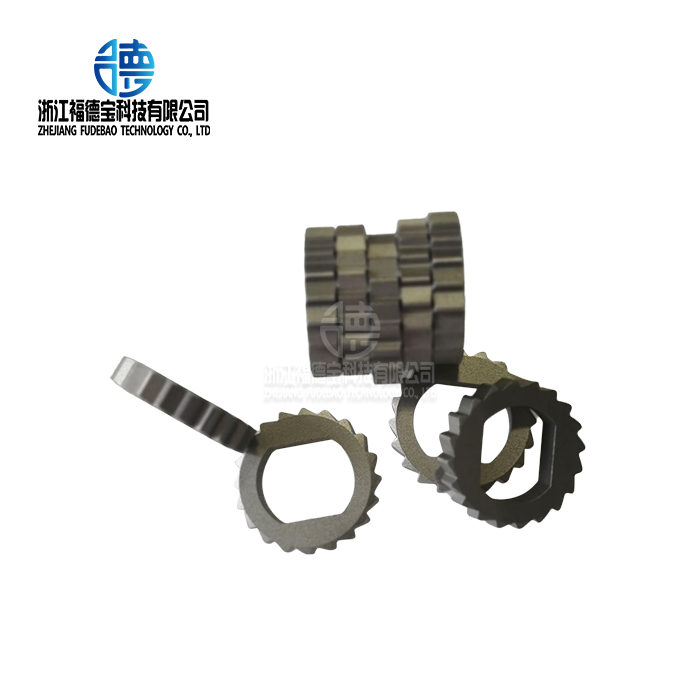
Sand-cast components are used extensively in a variety of manufacturing industries, including automotive and aerospace, because to their special blend of strength, complexity, and affordability. Engine blocks, gearbox housings, and suspension parts are examples of automotive applications where dimensional precision and weight reduction are critical. For gear cases, valve bodies, and pump housings that must survive harsh working conditions, industrial equipment makers use sand casting.
The options for choosing materials include almost every range of technical alloys. Copper alloys provide higher electrical conductivity for components used in the energy industry, while aluminum sand castings offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios for transportation applications. For large equipment applications where mechanical qualities are more important than weight, steel and iron castings provide outstanding durability.
Process Advantages and Engineering Considerations
Large, intricate geometries that would be prohibitively expensive to produce using other production techniques are best produced via sand casting. In a single casting operation, the method can handle complex internal features, undercuts, and different wall thicknesses. Sand casting is economically feasible for both prototype development and medium-volume production runs since tooling costs are still low when compared to die casting or investment casting.
However, while choosing a supplier, dimensional tolerances and surface finish quality must be carefully taken into account. Depending on the size and complexity of the item, typical sand casting tolerances vary from ±0.5mm to ±1.5mm, which may need additional machining processes for features that are crucial to accuracy. Procurement teams may create reasonable specifications and budgetary allotments for whole part processing by having a thorough understanding of these intrinsic features.
Essential Criteria for Selecting a Sand Casting Supplier
Technical Capabilities and Quality Certifications
Evaluating potential suppliers begins with assessing their technical infrastructure and quality management systems. While industry-specific certifications like ISO/TS 16949 for automotive applications or AS9100 for aerospace applications show particular competence, ISO 9001 certification offers baseline assurance of process control and documentation methods. Advanced suppliers exhibit thorough operational maturity by holding extra certifications for occupational safety and environmental management.
Delivery capabilities and component quality for sand casting are directly impacted by production equipment. In order to improve uniformity while lowering human error, modern foundries use computer-controlled pouring equipment, automated molding lines, and induction melting systems. Real-time quality monitoring throughout production cycles is made possible by metallurgical labs equipped with spectrometers, mechanical testing equipment, and dimensional inspection instruments.
Production Capacity and Scalability Assessment
As your manufacturing needs change, being aware of supplier capacity constraints helps you avoid bottlenecks in the future. To determine scaling possibilities, assess equipment usage rates, available floor space, and yearly tonnage capacity. While suppliers with significant unused capacity may have financial sustainability issues, those working close to full capacity may find it difficult to handle urgent orders or volume spikes.
Lead time analysis shows planning accuracy and operational effectiveness. Reputable vendors provide thorough project schedules that take into consideration the creation of patterns, the fabrication of molds, the casting process, and the final steps. When there are unforeseen demand surges or quality problems that need to be fixed quickly, emergency response skills become essential. Timely information on production progress and any schedule modifications are ensured by establishing explicit communication methods.
Geographic Proximity and Logistics Considerations
Lead times and transportation costs rise dramatically with distance, especially for large sand castings. Shorter delivery cycles, lower transportation costs, and easier logistical coordination are all benefits of using regional suppliers. However, as poor-quality components result in significantly higher costs than transportation savings, regional closeness shouldn't take precedence above basic quality and performance criteria.
Assessing suppliers' sources of raw materials, backup power systems, and emergency preparedness protocols are examples of supply chain risk mitigation techniques. Because production schedules might be disrupted by natural catastrophes, labor conflicts, or equipment problems, supplier variety is a crucial factor for important applications. Through supplier rivalry, dual-sourcing techniques preserve competitive price while insuring against single-point failures.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them When Working with Sand Casting Suppliers
Quality Control and Defect Prevention Strategies
Porosity, inclusions, dimensional irregularities, or surface flaws that impair component functioning are common signs of poor sand casting quality. poor process controls, tainted raw materials, or poor operator training are often the causes of these issues. Establishing precise specifications that include acceptable tolerance ranges, surface finish criteria, and mechanical property goals is the first step in proactive quality assurance.
Consistent quality monitoring throughout production runs is ensured by putting strong sample processes into place. While first article inspection techniques confirm material characteristics and dimensional correctness prior to full-scale production, statistical process control approaches assist in identifying patterns before they lead to nonconforming parts. Frequent supplier audits provide chances to analyze continuous improvement programs, examine quality records, and appraise facility conditions.
Communication and Project Management Best Practices
Delivery capabilities and component quality for sand casting are directly impacted by production equipment. In order to improve uniformity while lowering human error, modern foundries use computer-controlled pouring equipment, automated molding lines, and induction melting systems. Real-time quality monitoring throughout production cycles is made possible by metallurgical labs equipped with spectrometers, mechanical testing equipment, and dimensional inspection instruments.
In order to preserve traceability and facilitate future reorders, documentation requirements are essential. Dimensional drawings, material requirements, testing procedures, and packaging guidelines should all be included in thorough specifications. Change control processes guarantee that design changes are appropriately conveyed and carried out without posing a danger to quality or causing delays in the timeline.
Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Even with rigorous supplier selection and relationship management, supply chain disruptions may still happen. Maintaining production continuity in the face of unforeseen circumstances is facilitated by creating backup plans that include temporary quality relaxations, quicker shipment choices, and other suppliers. Assessments of financial stability guard against situations when suppliers go bankrupt or close their businesses, which might disrupt existing projects or strand vital equipment.
Throughout the casting process, many verification steps are necessary to avoid quality escape. Layers of defense against faulty parts arriving at client facilities are established by incoming material checks, in-process monitoring, and final dimensional verification. Clear responsibility matrices provide thorough coverage of all essential standards while defining responsibilities for different areas of quality.
Comparing Sand Casting to Other Casting Methods for Optimal Supplier Selection
Sand Casting vs. Die Casting Performance Analysis
Die casting is appealing for high-volume automotive and consumer electronics applications because it provides better surface finish quality and dimensional precision than sand casting. For low-volume or prototype applications, however, die casting tooling costs may be much higher than those of sand casting by a factor of ten or more. Die casting is mostly limited to non-ferrous alloys due to material constraints, but sand casting may be used with almost any castable metal.
Each process's economic feasibility is determined by production volume criteria. While sand casting is still competitive for numbers ranging from single prototypes to medium production runs, die casting becomes cost-effective at volumes reaching several thousand pieces yearly. For components with complicated interior geometries or changing wall thicknesses that complicate die casting tool design, sand casting is preferred due to part complexity concerns.
Investment Casting and Lost Foam Alternatives
Investment casting often removes the need for further machining because of its remarkable dimensional precision and surface finish quality. In contrast to sand casting, process constraints raise per-piece costs and limit item sizes. Although lost foam casting involves specific tools and methods that restrict supplier availability, it provides design freedom comparable to sand casting and greater dimensional accuracy.
Alternative casting methods differ greatly in terms of material compatibility. While investment casting works well for precise applications and superalloys, it becomes prohibitively expensive for big structural components. Aluminum and iron alloys are excellent candidates for lost foam casting, but copper-based materials pose difficulties because of their distinct solidification properties.
Process Selection Guidelines and Decision Matrices
It is necessary to systematically compare process capabilities for sand casting with part requirements in order to choose the best casting procedures. Initial screening is usually driven by volume concerns, and then dimensional tolerance analysis and material compatibility evaluation follow. While cost objectives set upper limitations for feasible production options, surface finish standards may preclude some processes.
By assigning scores to variables like tooling cost, piece price, lead time, and quality capability, decision matrices assist in quantifying trade-offs between competing process choices. Weighted scoring methods provide for objective comparisons that enhance data-driven procurement choices by accounting for various project components' differing priority levels. Sensitivity analysis shows how the best process choice may change when requirements change.
Our Expertise and Solutions in Sand Casting
Comprehensive Manufacturing Capabilities at Fudebao Technology
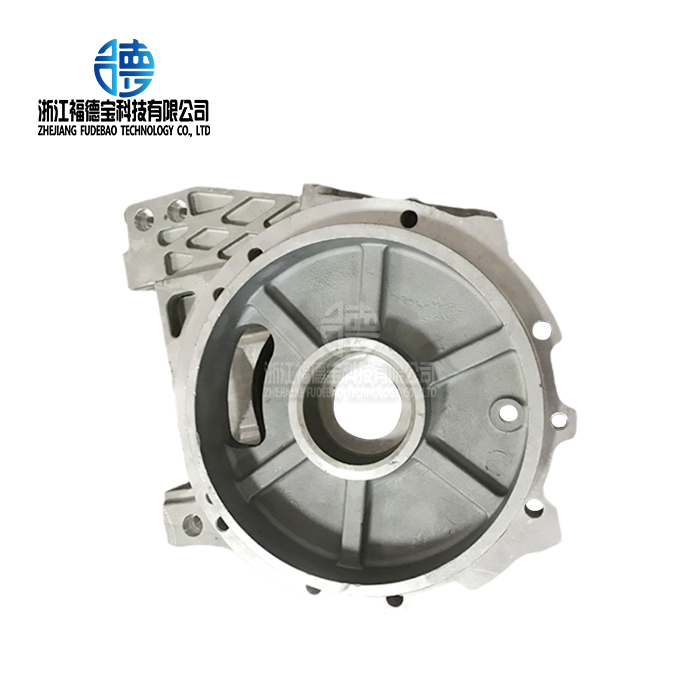
Zhejiang Fudebao Technology Co., Ltd. has made a name for itself as a top producer of casting solutions for stainless steel, copper alloy, and aluminum alloy. High-speed machining centers, CNC lathes, low-pressure casting machines, and die casting systems are among the cutting-edge tools in our state-of-the-art facility that enable whole production processes from raw material processing to final component delivery.
With melting, casting, finishing, and surface treatment activities all under one roof, our integrated approach covers the whole manufacturing spectrum. This all-inclusive capacity maintains strict quality control at every level of manufacture while removing the coordination issues related to multi-supplier setups. Precision machining capabilities fulfill the rigorous needs of medical equipment applications and automotive precision components, achieving tolerances up to ±0.05mm.
Our dedication to operational excellence and customer satisfaction is shown by the company's transition from middleman operations to direct supply agreements with well-known worldwide brands like HAAS automated machine tools and ESS energy storage systems. This change underscores our commitment to establishing enduring partnerships based on dependable performance and technological know-how rather than just affordable prices.
Industry-Specific Solutions and Quality Assurance
Automotive, industrial equipment, machinery manufacturing, and aviation applications are just a few of the many industrial sectors that make up our clientele. We use customized process development and quality management systems to handle the distinct technological problems and quality needs that each area brings. While aerospace clients depend on our certification systems and traceability processes, automotive clients benefit from our dimensional accuracy accomplishments and PPAP documentation capabilities.
In order to guarantee uniform part quality across all manufacturing batches, quality assurance infrastructure consists of extensive testing labs, dimensional inspection tools, and metallurgical analysis capabilities. During the design process, our team of skilled engineers collaborates closely with clients to choose the best materials, optimize casting shape, and set reasonable tolerance standards that strike a compromise between production viability and performance requirements.
Initiatives for continuous improvement concentrate on waste reduction, cycle time minimization, and process optimization, which result in lower costs and better delivery results for our customers. Before investing in actual equipment, advanced simulation software helps forecast casting behavior and improve gating systems, lowering development risks and speeding up time-to-market for new product launches.
Conclusion
A thorough assessment of technical prowess, quality control procedures, and production capacity in relation to your project's particular needs is necessary when choosing a sand casting provider. The choice affects long-term supply chain stability and cost competitiveness in addition to immediate part quality and delivery performance. When suppliers exhibit true industry knowledge while maintaining strong quality control procedures and expandable manufacturing capacities, successful collaborations are formed.
Supplier selection is now a continuous strategic consideration rather than a one-time procurement choice since the casting business is always changing due to technology progress and process innovation. Suppliers that make investments in cutting-edge machinery, keep up-to-date certifications, and gain specialized knowledge establish themselves as important long-term partners who may assist your company's expansion and product development endeavors.
FAQ
What are the usual lead times for projects using sand casting?
Based on part complexity, tooling needs, and production quantities, lead times for sand casting projects vary greatly. Production of simple aluminum castings using current tools usually takes two to four weeks, whereas sophisticated steel castings or the creation of new patterns might take up to twelve weeks. To assist you in making appropriate plans, suppliers have to provide comprehensive project schedules that delineate the steps of pattern development, trial casting, and production.
How can I assess possible sand casting vendors' quality capabilities?
Examining facility audits, supplier certificates, and client testimonials from related applications is the first step in evaluating quality. To evaluate surface polish, dimensional correctness, and general craftsmanship, ask for samples of similar items. Examine quality documents, such as process control charts, material certificates, and inspection reports. The best way to assess personnel skill levels, facility organization, and equipment condition is via on-site inspections.
What variables affect the price of sand casting in addition to the base piece?
Pattern creation, tooling changes, material specifications, secondary machining, surface treatments, and packaging needs are all included in the cost of sand casting. For large items or suppliers who are far away, transportation expenses become substantial. Additional testing, inspection, or documentation may be required to meet quality standards, which raises the project's total cost. Accurate supplier comparisons and realistic budgeting are made possible by having a thorough understanding of all cost components.
How can I be sure that the quality is constant over many manufacturing batches?
Establishing thorough specifications, putting statistical process control into place, and keeping in constant contact with your supplier are all necessary for consistent quality. Get quality control methods, inspection schedules, and process flow charts tailored to your items. Clearly define acceptance standards for material qualities, surface polish, and dimensional tolerances. Frequent performance evaluations and supplier audits aid in spotting areas for improvement and preserving quality standards over time.
Partner with Fudebao Technology for Superior Sand Casting Solutions
Are you prepared to use precise sand casting components to improve your manufacturing projects? Fudebao Technology offers outstanding quality and dependability for your vital applications by fusing state-of-the-art machinery with decades of foundry experience. Our dedication to continual development assures competitive pricing and reduced lead times, while our integrated production strategy promises smooth coordination from the first design consultation to the final delivery. To discuss your unique needs and discover the benefits of collaborating with a reputable sand casting manufacturer committed to your success, get in touch with our technical team at hank.shen@fdbcasting.com.
References
Campbell, John. "Complete Casting Handbook: Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design." Butterworth-Heinemann, 2015.
Brown, Jeffrey R. "Foseco Ferrous Foundryman's Handbook." Butterworth-Heinemann, 2000.
American Foundry Society. "Sand Casting Quality Management Guidelines for Industrial Applications." AFS Technical Publication, 2019.
Beeley, Peter R. "Foundry Technology." Newnes, 2001.
Stefanescu, Doru Michael. "Science and Engineering of Casting Solidification." Springer International Publishing, 2015.
Davis, Joseph R. "Cast Irons: ASM Specialty Handbook." ASM International Materials Engineering, 1996.
YOU MAY LIKE










_1756346421748.webp)


_1756348623524.webp)
_1756349146076.webp)


