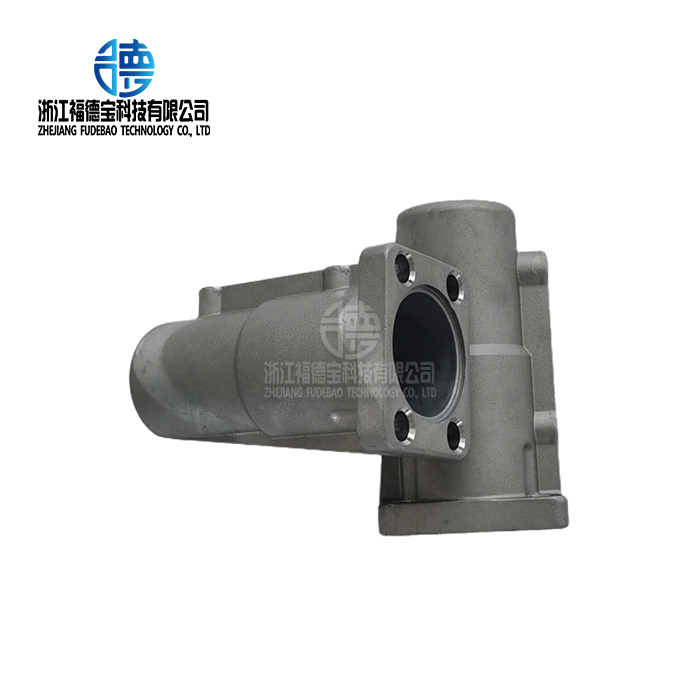
One of the most adaptable and popular metal casting techniques in contemporary production is sand casting. This thorough manual covers every facet of sand casting, from designing patterns to final finishing methods. Melted metal is poured into a sand mold chamber that corresponds to the finished component's intended form in a process known as sand casting. The method is useful for automotive, industrial equipment, and aerospace applications because it can handle complicated geometries, different kinds of alloys, and adjustable production quantities. Engineers may maximize component quality while preserving cost-effectiveness by comprehending the complex interaction between patterns, molds, and finishing procedures.

Understanding Sand Casting Fundamentals
Understanding the interactions between molten metal, binder systems, and sand during the solidification process is the cornerstone of effective metal casting. The most used molding material is still green sand, which is made up of silica sand combined with moisture content and clay binder. While retaining enough strength to hold molten metal in place after pouring, this combination offers exceptional moldability.
The exact control of sand characteristics, such as permeability, compressive strength, and thermal stability, is essential to foundry operations. By regulating metal flow rates and reducing turbulence, the gating system design has a direct effect on casting quality. Casting flaws including porosity, inclusions, and partial filling are decreased by properly positioned gates.
Throughout the casting cycle, temperature control is essential. The final microstructure, mold filling properties, and metal fluidity are all impacted by the pouring temperature. Engineers must strike a compromise between high temperatures that might break mold or coarsen grains and sufficient fluidity for full mold filling.
Pattern Design and Manufacturing Considerations
The foundation of dimensional accuracy in sand casting processes is an efficient pattern design. Depending on the kind of sand and the intricacy of the pattern, draft angles usually fall between 0.5 and 3 degrees. While too much draft might jeopardize dimensional standards, too little draft causes mold damage during pattern removal.
The alloy composition and casting geometry have an impact on shrinkage allowances in sand casting. Copper alloys may need 1.5–2.1% linear shrinkage allowance, while aluminum alloys usually require 1.0–1.3%. Both solidification shrinkage and thermal contraction during cooling must be taken into consideration by pattern creators.
Core requirements arise when internal cavities exceed what external molding can achieve. Core boxes must provide adequate venting to prevent gas entrapment during metal pouring. Core placement accuracy directly affects wall thickness uniformity and dimensional consistency.
Modern pattern manufacturing increasingly utilizes CNC machining for complex geometries requiring tight tolerances. Rapid prototyping and design iteration are made possible by digital pattern development, which also preserves dimensional repeatability across manufacturing batches.

Mold Assembly and Quality Control
Proper mold assembly techniques ensure consistent casting quality across production runs. Flask alignment prevents metal leakage and maintains dimensional accuracy. Cope and drag registration systems provide repeatable mold assembly while accommodating pattern removal requirements.
Mold strength and permeability properties are strongly influenced by the degree of sand compaction. While over-compaction minimizes gas escape pathways, under-compaction might lead to mold erosion during pouring. Consistent ramming techniques produce uniform sand density throughout the mold cavity.
Mold inspection procedures identify potential defects before metal pouring. Visual examination reveals cracks, loose sand, or incomplete pattern impressions. Correct core placement and cavity precision are confirmed by dimensional verification. Adequate venting for trapped air and gas evolution during solidification is ensured by gas permeability testing.
Riser design calculations determine feeding requirements for different casting sections. Proper riser sizing prevents shrinkage porosity while minimizing material waste. Riser placement considers solidification progression and thermal gradients within the casting.
Pouring Techniques and Process Optimization
Timing accuracy, flow rate management, and temperature control must all be carefully coordinated while pouring metal. Preheating to avoid thermal shock and degassing to eliminate dissolved hydrogen are two steps in ladle preparation. A proper pouring height ensures full mold filling while reducing turbulence.
Controlling the cooling rate has an impact on dimensional stability and mechanical characteristics. While slow cooling may provide coarse grain structure, rapid cooling may result in residual stresses and deformation. Controlled cooling techniques maximize dimensional precision and metallurgical qualities.
Process monitoring systems track critical parameters including pour rate, temperature profiles, and cooling curves. Data collection enables process optimization and quality trend analysis across multiple production batches.
Finishing Operations and Surface Treatment
Post-casting operations transform rough castings into precision components meeting final specifications. Shake-out procedures remove sand while minimizing casting damage. Automated shake-out systems improve efficiency while maintaining consistent sand recovery rates.
Gate and riser removal requires careful consideration of cutting methods and final surface requirements. Abrasive cutting provides rapid removal but may require additional finishing. Machining operations offer superior surface finish but increase processing time and cost.
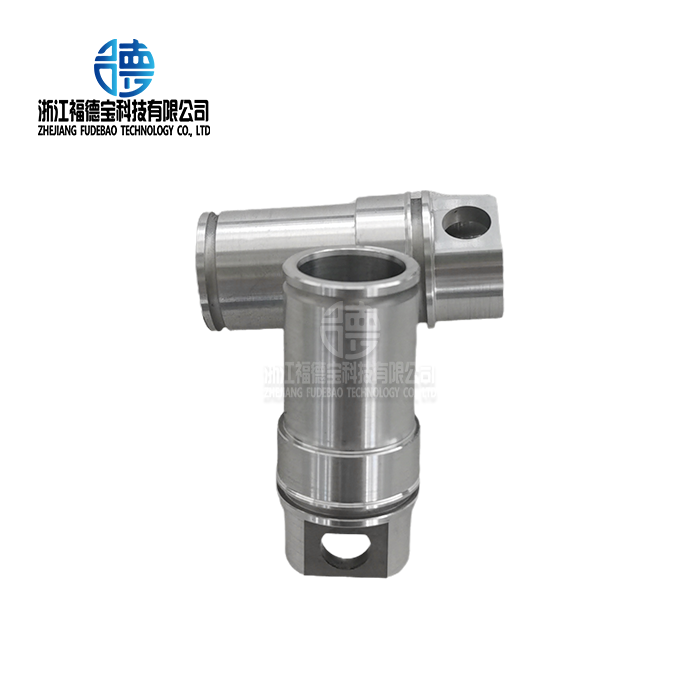
Techniques for improving surface polish vary from simple cleaning to intricate machining. Sand residue is eliminated and a consistent surface texture is produced by shot blasting. For essential surfaces that need to fit and operate precisely, CNC machining may reach final dimensions with tolerances as small as ±0.05mm.
In order to alleviate residual stresses or obtain the appropriate mechanical characteristics, heat treatment procedures could be needed.Solution treatment followed by artificial aging optimizes strength and hardness in aluminum alloys. Stress relief annealing reduces distortion potential during subsequent machining operations.
Quality inspection validates dimensional conformance and surface integrity. Complex geometries are verified to design standards using coordinate measuring equipment. Non-destructive testing techniques find intrinsic flaws that might compromise the dependability or performance of a component.
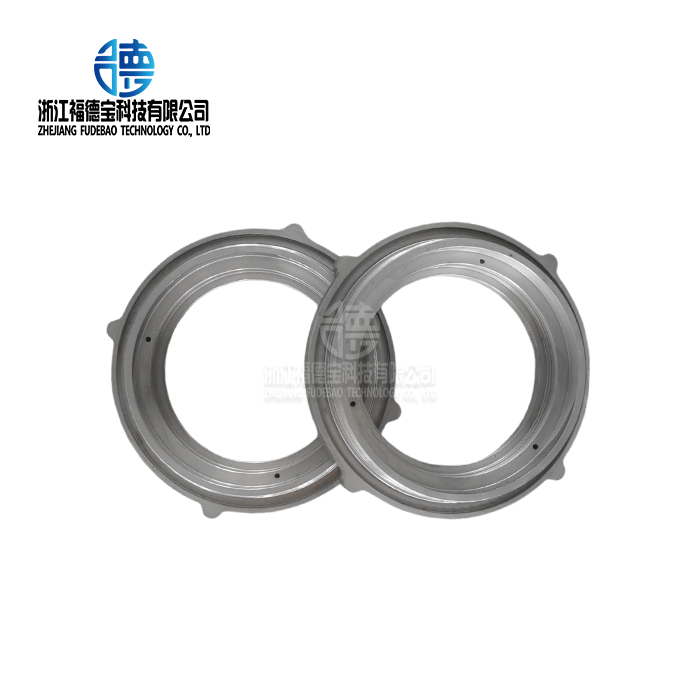
Industry Applications and Material Selection
Automotive applications demand lightweight aluminum castings with exceptional dimensional stability. Engine components require heat resistance and thermal cycling durability. Transmission housings need precise bearing surfaces and oil passage integrity. PPAP documentation ensures traceability and quality system compliance throughout component lifecycle.
Electrical and energy sector applications emphasize conductivity and thermal management properties. Motor housings provide electromagnetic shielding while facilitating heat dissipation. Electrical connectors require precise dimensions and surface conductivity. Renewable energy components face extended service life requirements under environmental exposure.
Aerospace and defense applications require comprehensive certification systems and material traceability. Advanced inspection techniques verify internal soundness and dimensional conformance. Tight-tolerance machining capabilities produce critical flight hardware meeting stringent reliability requirements.
Conclusion
Advanced materials, enhanced process control, and integrated quality systems have all contributed to the ongoing evolution of sand casting. Understanding the intricate relationships between pattern design, mold preparation, pouring methods, and finishing processes is essential for success. In order to keep the flexibility that makes sand casting so useful for a wide range of applications, modern foundries use technology to produce uniform quality. Whether manufacturing industrial equipment parts, automobile components, or aircraft gear, paying close attention to each step of the process guarantees the best possible outcomes. Investing in high-quality alliances with seasoned foundries gives access to cutting-edge capabilities and technical know-how necessary for competitive component manufacture.

Partner with Fudebao Technology for Superior Sand Casting Solutions
Quality sand casting manufacturer partnerships enable access to advanced capabilities and proven expertise across diverse industries. Fudebao Technology combines decades of foundry experience with state-of-the-art equipment including low-pressure casting machines, die casting systems, and precision CNC machining centers. Our integrated approach covers the complete production cycle from pattern development through final surface treatment.
Advanced quality systems ensure consistent results while meeting industry-specific requirements. Coordinate measuring equipment and non-destructive testing systems are among the extensive inspection capabilities that our institution maintains. Customer quality needs are supported by material certifications and process documentation in applications such as automotive, industrial, electrical, and aerospace.
Process development, material selection, and design optimization are all aided by engineering support services.Our technical team collaborates with customers to achieve optimal casting designs that balance performance requirements with manufacturing efficiency. Prototype development capabilities enable design validation before production commitment.
Production flexibility accommodates both high-volume automotive applications and specialized aerospace components requiring extensive documentation. Our sand casting capabilities complement die casting and CNC machining services for comprehensive component solutions. Complete supply chain management reduces customer procurement complexity while ensuring delivery performance.
Ready to explore how advanced sand casting capabilities can enhance your component requirements? Contact our technical specialists to discuss your specific application needs. Reach out to contact us at hank.shen@fdbcasting.com to begin developing your next casting project with a trusted sand casting supplier committed to excellence.
References
1. Campbell, J. "Complete Casting Handbook: Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design." Butterworth-Heinemann, 2015.
2. Brown, J.R. "Foseco Foundryman's Handbook: Facts, Figures and Formulae." Butterworth-Heinemann, 2000.
3. Beeley, P. "Foundry Technology." Newnes, 2001.
4. American Foundry Society. "Sand Casting Manual." American Foundry Society Publications, 2018.
5. Stefanescu, D.M. "Science and Engineering of Casting Solidification." Springer, 2009.
6. Flemings, M.C. "Solidification Processing." McGraw-Hill, 1974.
















_1756348711711.webp)
